# It is bad to install via pip into a conda environment. I know this
# Remove the commenting and run
# ! pip install odc-stac stac
# ! pip install geopolarsIntroduction to Geospatial Analyses in Python in the Cloud
This is based on the “Examining Environmental Justice through Open Source, Cloud-Native Tools” notebook from Carl Boettiger. Please follow Carl’s notebook for the background. This tutorial just focuses on the code.
Set up
You install a few things that are not on this JHub.
import odc.stac
import rioxarray
from pystac_client import Client
import geopandas as gpd
from rasterstats import zonal_stats
import dask.distributed
client = dask.distributed.Client()
odc.stac.configure_rio(cloud_defaults=True, client=client)Data discovery
Here we use a STAC Catalog API to recover a list of candidate data. This example searches for images in a lon-lat bounding box from a collection of Cloud-Optimized-GeoTIFF (COG) images taken by Sentinel2 satellite mission. This function will not download any imagery, it merely gives us a list of metadata about available images.
box = [-122.51, 37.71, -122.36, 37.81]
items = (
Client.
open("https://earth-search.aws.element84.com/v1").
search(
collections = ['sentinel-2-l2a'],
bbox = box,
datetime = "2022-06-01/2022-08-01",
query={"eo:cloud_cover": {"lt": 20}}).
item_collection()
)We pass this list of images to a high-level utilty (gdalcubes) that will do all of the heavy lifting:
- subsetting by date
- subsetting by bounding box
- aggregating by time
P1D - reproject into the desired coordinate system
- resampling to a desired spatial resolution
data = odc.stac.load(
items,
crs="EPSG:4326",
bands=["nir08", "red"],
resolution=0.0001,
bbox=box
)Calculate NDVI, a widely used measure of greenness that can be used to determine tree cover.
red = data.red
nir = data.nir08
ndvi = (((nir - red) / (red + nir)).
resample(time="MS").
median("time", keep_attrs=True).
compute()
)
# mask out bad pixels
ndvi = ndvi.where(ndvi <= 1)Plot the result. The long rectangle of Golden Gate Park is clearly visible in the North-West.
import matplotlib as plt
cmap = plt.colormaps.get_cmap('viridis') # viridis is the default colormap for imshow
cmap.set_bad(color='black')
ndvi.plot.imshow(row="time", cmap=cmap, add_colorbar=False, size=5)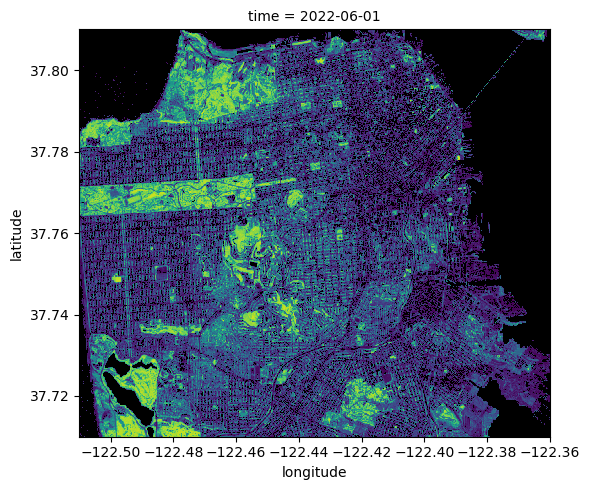
Add the 1937 “red-lining” zones from the Mapping Inequality project. The red-lined zones are spatial vectors.
ndvi.rio.to_raster(raster_path="ndvi.tif", driver="COG")
sf_url = "/vsicurl/https://dsl.richmond.edu/panorama/redlining/static/citiesData/CASanFrancisco1937/geojson.json"
mean_ndvi = zonal_stats(sf_url, "ndvi.tif", stats="mean")Now we can plot
sf = gpd.read_file(sf_url)
sf["ndvi"] = [x["mean"] for x in mean_ndvi ]
sf.plot(column="ndvi", legend=True)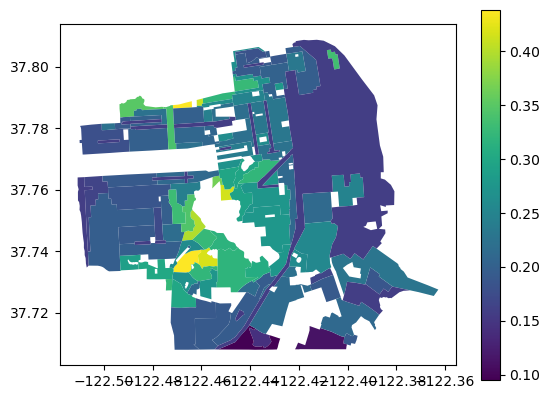
Compute the mean current greenness by 1937 zone.
import geopolars as gpl
import polars as pl
(gpl.
from_geopandas(sf).
group_by("grade").
agg(pl.col("ndvi").mean()).
sort("grade")
)| grade | ndvi |
|---|---|
| str | f64 |
| null | 0.157821 |
| "A" | 0.338723 |
| "B" | 0.247344 |
| "C" | 0.231182 |
| "D" | 0.225696 |